In today’s digital world, bandwidth is critical in ensuring smooth internet operations and website functionality. Whether you’re a website owner or a user, encountering a “Bandwidth Limit Exceed” error can be frustrating. This issue makes websites offline and harms the usability and functionality of the sites for business ventures.
It is, therefore, essential for anyone in charge of managing online platforms to know what leads to these limits being surpassed and how the matter may be solved. In this blog post, we’d like to talk about the most frequent causes of bandwidth limit exceed and share tips on how to solve and avoid such problems.
Understanding Bandwidth and Its Importance
Bandwidth is the maximum rate at which data can be transferred across a network path. Imagine the width of a highway; the broader the road, the more vehicles it can accommodate simultaneously. Regarding internet functionality, bandwidth determines how much data can be exchanged between your website’s server and its users.
High bandwidth is essential, especially in terms of loading time because when there is much data to transfer, the transmission has to be fast. On the other hand, the low bandwidth can lead to slow downloads, frustrating the user and possibly demotivating him from continued use of the website. It also impacts on the efficiency and credibility of your site.
Lack of sufficient bandwidth negatively impacts the effectiveness of web applications and other high-bandwidth programs, including streaming services. Learning about bandwidth and its importance positions you well to make the right hosting choices as well as the general experience of the website users.
Common Causes of Bandwidth Limit Exceed
Several factors can contribute to exceeding your bandwidth limit. A sudden spike in traffic, such as when a website goes viral or receives significant media attention, can quickly consume available bandwidth. Large files like high-resolution images, videos, or downloadable content significantly increase bandwidth usage. Inefficient website design or coding practices may lead to excessive data transfer and straining limits.
Hotlinking, where other websites directly link to your site’s resources, can drain bandwidth. Additionally, poorly optimized plugins or scripts running on your site can generate unnecessary data traffic. This allows one to discover some general phenomena that may contribute to bandwidth usage and take corrective measures as far as their impact on bandwidth usage is concerned.
Monitoring Bandwidth Usage
To effectively manage bandwidth and prevent exceeding limits, it’s essential to keep an eye on your usage. We could use services like Google Analytics, AWStats, or server logs to determine how much bandwidth your site uses and when that is optimal.
When you have this data analyzed, it is recommended that it be reviewed frequently to identify abnormal trends that cause problems. A bandwidth notification is valid when it lets you know when you are close to the set limit so you can get to work.
By using such monitoring techniques, one is not only able to prevent such problems from happening but also get an insight into how your site is faring as well as user behavior. This way, you are placed in a vantage position to take specific and strategic decisions improving the bandwidth utilization pattern in your organization.
Optimizing Website Content
One effective way to manage bandwidth usage is by optimizing your website content. Compressing images and videos can significantly reduce the amount of data transferred. For this, some illustrative applications such as Photoshop or TinyPNG or online compression applications can be used to reduce size.
Further, reducing one’s usage of large files and practicing ways to find more efficient data storage methods can also work. Correctly formatting your text and images for the web can ensure your site loads faster and uses less bandwidth. Reducing the number of high-resolution photos and opting for lightweight formats like JPEG and WebP instead of PNG can make a noticeable difference.
Videos can be hosted on external platforms like YouTube or Vimeo to save on your capacity. Efficiently coding your website is another crucial step. Clean, streamlined code loads faster and uses less bandwidth. Avoid unnecessary scripts and excessive plugins that can slow down your site and increase data transfer.
Utilizing modern web development practices like lazy loading, where images and videos load only when they come into the user’s viewport, can further optimize bandwidth usage. Last but not least, the use of CSS sprites that enable the use of several pictures in a single file decreases general HTTP requests, therefore increasing speed and bandwidth usage. These optimization strategies help improve the overall quality of your site while also making it easier to respond to high traffic without pushing past your capacity.
Implementing a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) can significantly enhance your website’s performance by distributing your content across multiple servers worldwide. By caching your website’s static assets like images, stylesheets, and scripts, a CDN ensures that these elements are delivered from the server closest to the user’s location.
This geographical distribution minimizes latency, the delay before a data transfer begins following an instruction, thereby speeding up load times. Additionally, a CDN reduces the bandwidth load on your primary server, allowing it to handle more dynamic requests efficiently. Popular CDN providers include Cloudflare, Akamai, and Amazon CloudFront, each offering various features tailored to different needs.
Integrating a CDN is generally straightforward; most providers offer easy-to-follow guides for setup. Besides bypassing the user requests through the CDN, you also get the ability to protect against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which can otherwise tie up considerable bandwidth. CDNs also often provide analytical tools that may help evaluate your site and its visitor’s activity. CDN allows for successful implementation, enabling efficient bandwidth usage while positively affecting load time and site availability.
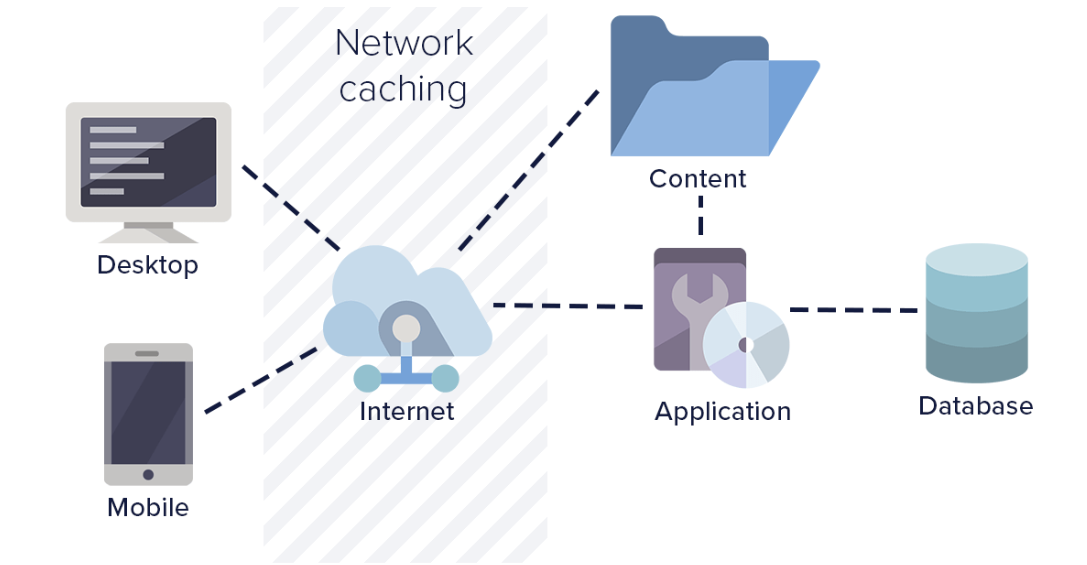
Utilizing Caching Mechanisms
Caching involves storing copies of your website’s data temporarily to reduce server load and bandwidth usage. Browser caching allows frequently accessed files to be stored locally on a user’s device, reducing the need to fetch them from the server repeatedly. Server-side caching solutions, like Varnish or Memcached, can store copies of dynamic content, serving it more quickly to users.
This means that conventional forwarding saves your server bandwidth since it doesn’t need to handle the same request several times.
Application and usage of cache mechanism is a guaranteed way of improving load time and overall performance of websites. One effective method is to set appropriate cache headers, which tell browsers and intermediary caches how long to store copies of resources. This is useful in situations where, for instance, you have many images, CSS files, and JavaScript. Moreover, the use of object caching in your database will improve query responses, hence enhancing the speed of your site.
Other WordPress sites use plugins such as W3 total cache or WP super cache to carry out some of these caching tasks on the site administrator’s behalf. As some of the data processing is performed by user devices and intermediary servers, caching not only saves bandwidth but also improves usability: your site will be more reliable during high traffic.
Upgrading Your Bandwidth Plan
Despite your best efforts to optimize and manage bandwidth, you might find that your current plan simply doesn’t meet your needs. In such cases, the only solution to the problem can be relocating the bandwidth plan to a higher one, which can accommodate the higher amount of traffic and data transfer.
Finally, talk to your hosting provider about your using patterns and expected future traffic. They can propose different plans containing different packages with different bandwidth availability while your site is visited for various periods.
As you make your decision to make the switch, we encourage you to make a proper evaluation of your website’s needs. It means how aggressively you are using the service currently and how aggressively you expect it will grow in the future.
This will assist you in determining which plan will work best for your needs now and when your traffic increases beyond your expectations. Moreover, some hosting providers provide multiple plans and options where you can adjust the bandwidth for your website easily to accommodate your needs where necessary, and mainly cheaper than going for a large bandwidth plan when you do not need it.
It is also essential to peruse the reviews of the customers and learn what distinctive characteristics the plans offer and at what rates they are to be had. There may also be extra features, which a hosting provider may provide and which are worth the cost for your hosting plan. Therefore, you should take your time and choose a good strategy that will suit your website’s functions without any buffering or limits on the bandwidth used.
Conclusion and Best Practices
Effectively managing your website’s bandwidth is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and user satisfaction. First, you should develop a clear picture of the bandwidth requirements for your specific site and then constantly supervise your rates using, at the least, applications like Google Analytics or server logs.
Reduce loading time by minimizing HTML and CSS, saving images in the correct format, and linking to video streams instead of embedding. Implement a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to distribute your content globally, reducing latency and bandwidth load on your primary server. Leverage caching mechanisms to store frequently accessed data, conserving bandwidth and improving load times.
Lastly, if your bandwidth usage starts to increase, it may be helpful to promote a better plan that will allow your site to handle the load. Implementation of these best practices will ensure you have a more robust and optimized web presence that will initially be capable of delivering quality services at peak usage.