When it comes to server storage, it is quite crucial to select the proper technology to enhance the performance and efficiency as well as overall system response time. Conventionally, HDDs and SSDs have largely shaped the outlook and each comes with benefits as well as downsides. However, the appearance of NVMe has changed all this and is an approach to server storage. This blog post will elaborate on why NVMe server storage is better than SSD and HDD by comparing the NVMe server storage system with the two devices in terms of speed and performance, efficiency, and potential for future advancement.
Understanding the Basics of NVMe, SSD, and HDD Technologies
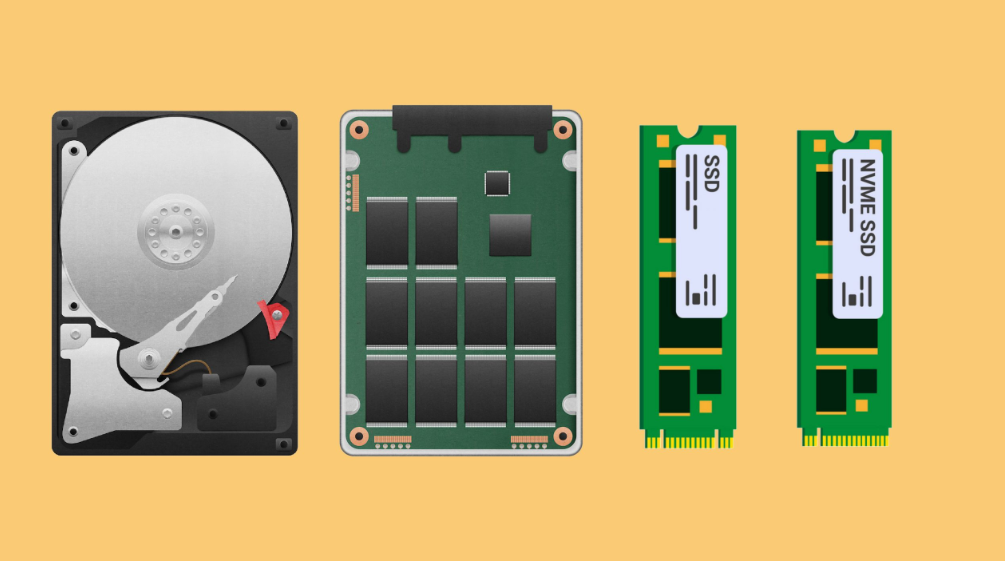
HDDs, or Hard Disk Drives, are mechanical devices that use spinning disks and read/write heads to store and retrieve data. They offer larger storage capacities at a lower cost per gigabyte but suffer from slower data access speeds due to their reliance on moving parts. This mechanical nature makes them less suited for high-speed data processing tasks, which can be a bottleneck in modern server environments.
SSDs, or Solid State Drives, use flash memory to store data, eliminating the mechanical components found in HDDs. This leads to improved data retrieval time and hence, reduced latency levels on the web. Nevertheless, it is imperative to note that a majority of today’s SSDs rely on the SATA (Serial ATA) interface, which was originally developed for application in Hard drives.
Although this interface has advanced in recent years it sets a ceiling on the overall bandwidth of SSDs. NVMe or Non-Volatile Memory Express is a hardware interface standard that was built from scratch for use with modern NAND Flash storage media which have initially low latency and concurrent command queuing.
Unlike SSDs that connect via SATA, NVMe drives connect directly to the motherboard through the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) bus. This direct connection allows NVMe drives to offer significantly higher data transfer rates and more efficient command processing, making them a superior choice for demanding server storage applications.

Speed and Performance Benefits of NVMe Over SSDs and HDDs
When it comes to speed and performance, NVMe server storage stands head and shoulders above traditional SSDs and HDDs. NVMe drives leverage the high-speed PCIe interface, enabling read and write speeds that can surpass 3,500 MB/s. In stark contrast, the fastest SATA SSDs typically peak at around 550 MB/s, and HDDs lag even further behind.
This substantial speed advantage translates to faster boot times, quicker data retrieval, and more responsive applications. For highly I/O demanding processes such as virtualization, databases, or big data affairs, the high speed of NVMe is revolutionary. These applications tend to involve the need to read and write big data in the shortest time possible and with NVMe being a solid performer in this capacity it can significantly cut down turnaround time.
This implies that organizations are in a good position to reap maximum value from the computational resources hence making the IT environment more responsive to current trends. In addition, the enhancement due to the implementation of NVMe also improves the system interactivity in totality and is even more advantageous where the activity consists of rapid data analysis.
NVMe then allows servers to process a higher number of tasks quickly without slowing down the operations or the experiences of the businesses or users.
Enhanced IOPS and Bandwidth for Server Applications
NVMe technology dramatically enhances Input/Output Operations Per Second (IOPS), a critical metric for server storage. Thanks to its parallel architecture, NVMe supports thousands of IOPS, processing multiple queues and commands simultaneously. This capability is especially beneficial to large-scale data warehouse applications where online transaction processing requires immediate and responsive data storage and query.
Compared to SATA SSDs, which typically support around 100,000 IOPS, NVMe’s performance is significantly higher. This makes NVMe drives exceptionally suited for tasks requiring high-speed, low-latency operations. HDDs, on the other hand, fall far behind in IOPS capabilities, making them less suitable for modern high-performance computing environments.
Additionally, NVMe leverages the high bandwidth available through PCIe connections to handle larger data volumes concurrently. This also comes in handy for high-performance computing and data-heavy tasks such as data analysis and machine learning whereby throughput integrity is paramount.
Nonetheless, the integral characteristics of density and stability of NVMe drive IOPS / bandwidth compliance with the requirements of modern server surroundings as well as efficient data management.
Lower Latency and Higher Efficiency in Data Processing
One of the standout advantages of NVMe server storage is its exceptionally low latency. Unlike traditional SSDs that connect via SATA interfaces, NVMe drives benefit from direct PCIe connections, which eliminates intermediary bottlenecks and significantly reduces latency. This capability helps to guarantee that any request for data is processed within only microseconds making applications faster. These low values are essential for real-time applications which include video streaming, online gaming, and high-frequency trading.
In such cases, even the slightest of the delays can prove critical to user experience or organizational efficiency. It has been observed that latency plays an important role in determining processing speed and real-time data accessibility; NVMe storage ensures that the process runs at high speed and the service is delivered without any interruption.
The savings in terms of the latencies also accumulate to the entire server climate. Faster data processing also results in less waiting time for the server hence there is efficient utilization of the various resources we have in the servers thus making it more efficient. This is particularly useful in situations where there is a need for heavy computations to be made, multi-threaded applications whereby there is a need for frequent access to a large data set.
In addition, the low latency of the NVMe enhances data processing and therefore is helpful in energy efficiency. This leads to a shorter data response time where servers can perform their tasks within a faster time hence cutting down the energy and operational costs. This makes NVMe not only a superior performance solution but also a power-efficient solution for today’s data centers.
Scalability and Flexibility for Growing Server Needs
This also means that as an organization grows its storage needs also grow and require solutions that can mimic this growth. NVMe server storage perspective provides the ultimate ability to expand and easily manage the data storage capacity without redesigning the system.
There are multiple interface choices such as M. 2 and U. 2 interfaces through which multiple NVMe drives can be installed with a single server for the easy expansion of storage components. It also enables businesses to scale up their storage capacity by adding more NVMe drives instead of swapping out the whole storage infrastructure.
Also, NVMe has better features compared to other interfaces like SCSI including namespace management, which allows for better control of the storage resources. That is helpful for multi-tenant environments and virtualized systems where sometimes different types of workloads will be needed. NVMe also makes power consumption intelligent so that incorporating more storage will not lead to high power costs which in return makes it a perfect choice for extending data centers.
In addition, NVMe has the scalability to support future technologies and standards for storage in today’s computing, which means current investments are not going to become ineffective as technology progresses. This forward compatibility indicates that organizations are free to deploy NVMe since their storage systems will be future-proof to support emerging technologies.
Overall, through the scalability and flexibility of the solution, NVMe guarantees that rapidly growing companies will be able to address different demands for their data appropriately.
Cost Considerations and Return on Investment
While the initial cost of NVMe server storage can be higher than that of traditional SSDs or HDDs, the long-term return on investment (ROI) can be substantial. NVMe drives operate at high speeds and performance to increase organizational efficiency and decrease processing time required to perform a task and end up being cheaper as well as offering a better experience to the users.
Also, NVMe drives are more lasting and less prone to fail than SATA Hard drives and therefore require minimal replacement and maintenance which, in turn, stylesheet maintenance expenses. Another benefit of NVMe is energy efficiency which significantly contributes to cost reduction. This means that smaller energy consumption allows data centers to save a lot of money on power costs in the future.
Hence, it is most advantageous for mass-scale productions where expending a lot on electrical power might considerably hurt. Moreover, as it was indicated earlier, NVMe is scalable and flexible, hence businesses can expand the scale of storage infrastructure as often as required without major overhauls that often are costly, thus minimizing capital expenses.
All in all, it can be mentioned that NVMe entails a higher initial cost from an organizational perspective; nevertheless, the gains registered in terms of performance, lower energy consumption, and higher reliability make NVMe a cost-efficient option for businesses that seek to optimize their information technology budgets and obtain superior value in the long run.
Industry Adoption and Future Trends in Server Storage
The implementation of NVMe technology has grown exponentially in the current years in such sectors as the financial sector, healthcare services, and cloud service. Large cloud services and data center providers are adopting NVMe storage into their systems to handle the current and future demand of data-centric, high-performance workloads.
The use of NVMe is prompted by high speed, low latency, and high throughput which is crucial in processing real-time data and big data analytics. For instance, with the help of NVMe, which has such features as the ability to deliver fast and reliable access to data, industries, which include online retail and financial services, are benefiting.
Finally, moving forward, the improvements of NVMe technology are expected to go on with new features such as NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF). This advancement expands on the high performance of NVMe across networked storage environments but adds increased scale and versatility to the equation. Thereby NVMe-oF extended the capacity to establish efficient distributed storage systems with the transfer of NVMe commands across various types of networks.
Moreover, future advancements are expected for more power-saving modes of NVMe alongside the incorporation of new generations of technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning. These improvements will help NVMe to establish itself further and become a standard solution for the further needs of server storage. NVMe is seen to be on the rise as companies remain focused on improving the speed and efficiency of their networks.
This trajectory guarantees NVMe will remain an important component in the design of the future of server storage, meeting the new and progressive needs of present and future organizations.