Introduction to Different Marketing Strategies
Businesses continuously explore practical ways to connect with their audience in the dynamic marketing landscape. Inbound and outbound marketing are among the myriad strategies due to their contrasting methods and objectives.
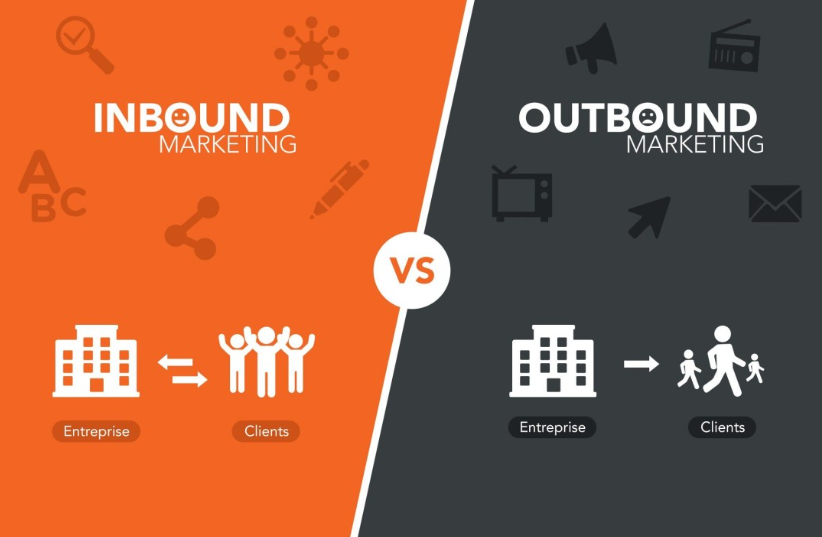
Inbound marketing is all about capturing the interest of prospective clients through the publication of valuable and applicable content. It raises people’s attention with information that they consciously look to receive.
On the flip side, outbound marketing adopts a more direct tactic, reaching out to potential customers through proactive promotions and advertisements. The strategies involved in this area aim to grab attention and encourage immediate action.
To effectively manage the goals of their marketing strategies, there must be a clear understanding between inbound and outbound marketing. Some associated tools and techniques are part of their global strategies, reflecting the rationale of each approach.
For example, inbound marketing utilizes content marketing, SEO, and social media to attract and engage an audience organically. On the other hand, outbound marketing, also called interrupt marketing, uses techniques like TV adverts, phone calls, and even commercial mail to market the brand.
Realizing these fundamental differences will enable assessing the strategy’s environment and deciding on a practical strategy that aligns with the firm’s goals and clients. From an understanding of inbound and outbound marketing and their differences, one will understand how inbound and outbound marketing can be used to further various specific marketing goals.
Approach and Methodology Overview
Inbound marketing centres on attracting potential customers by creating valuable and relevant content that fits their needs and interests. It perhaps tries to persuade people with what they are looking for, including tools such as content marketing, SEO and social media. In contrast, channelling its effort on organic attraction, inbound marketing seeks to establish a trusting, long-term relationship with consumers so that the latter actively come seeking the brand.
On the other hand, outbound recourse to its audience is done through a more conventional approach. It includes making direct calls to prospects for sales and other forms of direct communication. The purpose is to grab the audience’s attention quickly and get a quick response. Some examples are TV advertisements, cold calling, and offline advertising. This approach targets consolidating a large audience and strikes for quick responses or first sales.
Each works with different methods and approaches corresponding to the goals set before them. Inbound marketing is highly geared towards providing informative content that answers questions or solves a problem and thus attracts whom the content is targeting. On the other hand, outbound marketing tries to leave such an impression in the minds of its audience by using forceful and aggressive tones, which are meant to evoke prompt responses from the target demographic. These differences are anchored on the basic concepts of each style, defining how ventures interact with interested customers.
Channels and Techniques Explored
Inbound marketing harnesses various channels to draw in consumers naturally. Blogs are essential pieces that provide the necessary information to help a client solve his pain. This content must be easily findable, which is what Search Engine Optimization (SEO) does. Social media offers places where brand-committed communities can gather. It can also be used for lead nurturing when the business communicates to subscribers through email.
Outbound marketing, on the other hand, utilizes more traditional channels. Television and radio ads are staples, delivering direct messages to a broad audience. Cold calling involves reaching potential customers to pitch products or services directly. Although less common in today’s digital era, direct mail offers a tangible way to reach consumers with promotional materials. This also includes printing ads in newspapers and magazines targeting a given population.
Another type of outbound technique is event marketing, which includes trade shows and sponsorships to grab the attention of users or potential customers right from the start. Online display ads and pop-ups are digital extensions of outbound tactics designed to capture attention quickly.
Engaging the Target Audience
Inbound marketing focuses on building meaningful connections with the audience through content that addresses their needs and interests. The specific interaction activity utilized in this approach includes comment, social interaction and sharing.
If content is created with the targeted audience in mind, the business creates a fan base for the brand. Hence, long-term relationship-building helps in branding the site. It makes it a site where people regularly visit to learn more about the associated brand.
On the contrary, outbound marketing prioritizes swift actions and immediate engagement. Techniques such as television ads, cold calls, and direct mail are designed to grab attention quickly and prompt potential customers to take immediate steps, like purchasing or signing up for a service.
Unlike relationship marketing, the emphasis is on a single direct response rather than a long-term one. Outbound techniques typically use forceful sales appeals to make quick sales, thus keeping the brand in the consumer consideration set.
Yet another domain where outbound strategies excel is event marketing. Trade shows and sponsorships are effective as these are directly linked to people’s interests and make them immediately take action. Such events also allow firms to meet customers directly and market their products and services, receiving on-the-spot reactions.
Online display ads and pop-ups also fall under outbound tactics, aiming to quickly capture the audience’s attention. These methods are typically more assertive in converting prospects rapidly. While inbound marketing nurtures relationships through valuable content, outbound marketing aims for rapid engagement and quick conversions. Each approach appeals to the target audience differently and has strengths best applied to specific marketing goals.
Cost and ROI Analysis
Cost efficiency and return on investment (ROI) vary significantly between inbound and outbound marketing. Inbound marketing can entail producing and promoting content that uses digital search marketing, which can be relatively cheap in the long run. Once the initial content is created, it can continue to attract and engage customers with minimal additional costs. This makes inbound marketing a more sustainable long-term strategy, as it builds a lasting asset that generates ongoing traffic and leads.
Outbound marketing, in contrast, generally requires higher upfront costs. Channels like television ads, direct mail, and cold calling involve significant expenditures for media buys, production, and distribution. These costs can add up quickly, making it a more expensive approach. However, the immediate impact of outbound campaigns can sometimes justify the higher expense, especially for businesses needing rapid results.
While inbound marketing’s ROI can grow over time as the content gains traction, outbound marketing’s ROI is often more immediate but can taper off without continued investment. For businesses with budget constraints, the higher cost per lead in outbound marketing can be a limiting factor.
Therefore, the financial aspect of choosing between inbound and outbound marketing strategies hinges on balancing the initial costs with the expected timeframe for returns and aligning these with the overall business objectives.
Metrics and Analytics for Success
Metrics and analytics play a crucial role in evaluating the success of both inbound and outbound marketing strategies. Key performance indicators (KPIs) often include website traffic, user engagement, lead generation, and conversion rates for inbound marketing.
There are literally many monitoring programs out there, including Google Analytics or HubSpot or even other more specific monitoring programs, designed to show you which pieces of content your users are wasting their time on, which ones are driving the most traffic to your website, or which ones are the best at turning your website visitors into leads.
The goals outlined here are helpful for marketing professionals to adjust their approaches to ensure these audiences are well-served and to increase the efficiency of their campaigns with the hours being tracked in more effective methods for a given audience.
On the other hand, outbound marketing relies on more immediate metrics to gauge effectiveness. These can include response rates to direct mail campaigns, click-through rates (CTR) on digital ads, and the number of leads generated from cold calls.
TV and radio ads typically define success in terms of coverage, the number of times the advertisement was aired, and Gross Rating Point (GRP), the number of people who received the message. Measuring these metrics is supporting organizations in understanding the immediate results of outbound activities and modifying strategies that are not effective.
In this way, businesses may adapt to these measurements, employing the right tools for their evaluation, such as CRM for the lead source identification or analytics of the given advertising platforms. The beauty is that these KPIs should be measured and monitored frequently to ensure ever-improving marketing campaign performance and, thus, greater marketing return on investment.
Selecting the Appropriate Strategy
Selecting the right marketing strategy involves assessing your target audience, business objectives, and resource availability. Therefore, inbound marketing is most suitable for organizations requiring gradual marketing and building customer relationships. This is particularly appropriate when customers are often willing to consult online information and interact with related content before deciding.
On the other hand, outbound marketing is more appropriate when the first vision is required and the response is expected as soon as possible. This is suitable for businesses introducing a new product or service that needs the urgent attention of as many people as possible. It is particularly effective in industries that rely on direct marketing to convert clients within the shortest time possible and, thus, a worthwhile strategy.
However, companies use both inbound and outbound strategies to achieve the best outcomes. This keeps them receiving the benefits of the two styles and gets a form of marketing that can meet different goals and users’ patterns. Therefore, this work has revealed that combining the strengths of both approaches is crucial in fulfilling the company’s marketing objective of reaching the target customer.