It is clear, therefore, that in today’s business action and entrepreneurship, data storage is a significant area that defines success or lack thereof in business. Deciding which RAID levels to go for is not easy, and anyone can make it on a whim. RAID can be described as a Redundant Array of Independent Disks. This technology enables several hard disk drives in the server to be arranged to enhance its performance and storage capacity, in addition to offering backup for data. In this blog post, I will explain how to ease the decision-making process to select the most suitable RAID level for your server.
Understanding RAID Levels and Their Key Features
RAID technology refers to several arrangements that fulfill the need for data storage at a particular objective level. RAID configurations lie at the base and encompass RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10, with each configuration offsetting an enhanced characteristic of performance, capacitive storage, and protection.
RAID 0 has data striping as its chief feature that helps raise the speed factor enormously, but it has no backup option, which is a big no-no if your data is important to you. On the other hand, RAID 1 is characterized by mirroring data across the drives, making it probably one of the most fault-tolerant systems. At the same time, it retains only half the storage capacity of the total hard disk slash size.
RAID 5 brings in distributed parity, which gives an optimal solution rather than the two extremes of RAID 0 and RAID 1, providing better performance and additional data protection facilities with minimal loss of disk space. RAID 6 takes this even a notch higher by adding second-level redundancy, which improves the level of fault tolerance at the cost of slightly lower disk utilization and higher MIPS cost.
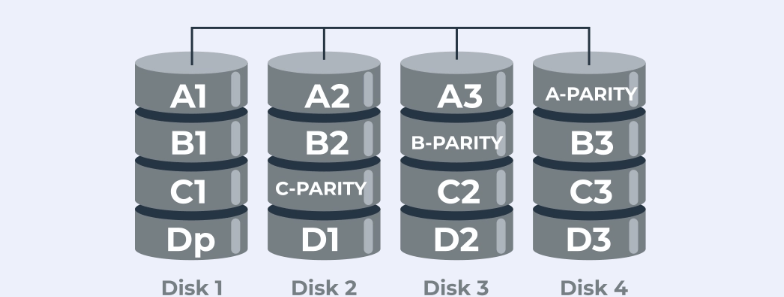
RAID 10 incorporates features of RAID 1 and RAID 0, where data is both striped and mirrored to provide fast data access and data redundancy; it is best suited for organizations that need fast data access with high levels of data availability. Understanding these prerequisites is crucial to achieving a RAID configuration that complements your business house’s requirements and constraints concerning performance, redundancy, and cost.
Assessing Your Business’s Data Storage Needs
Evaluating your business’s data storage requirements is a foundational step in selecting an appropriate RAID level. This involves a detailed analysis of several critical factors. First, quantify the volume of data your business generates and stores.
This aids in determining the capacity that is required and the RAID level that is not expensive but will serve the purpose. Second, evolve the criticality of your data. As an extension of this, you should also assess the criticality of the data you are collecting and processing – how much of it you can not afford to lose easily if the data falls into the wrong hands. This assessment helps to segment the requirement for data redundancy to back up the system, to protect the data.
Secondly, measure the requirements concerning the performance constraints of the business applications and services. Some operations may require faster access to the data, which will dictate the choice in favor of the RAID levels with better performance characteristics. Another important consideration is growth estimates, which is why it is known as the market growth rate. Anticipate increases in data volume and performance requirements to ensure the RAID level chosen today will still be adequate tomorrow.
Finally, understanding the nature of your data is crucial. Data that is frequently accessed and modified may benefit from a RAID level with higher performance and redundancy. In contrast, static data that doesn’t change often could be stored on a RAID configuration optimized for capacity. Through thoroughly assessing these factors, businesses can decide on the RAID level that best fits their unique data storage needs.
Performance vs. Redundancy: Striking the Right Balance
In the quest to choose the right RAID level, businesses often find themselves at the crossroads of prioritizing either performance or redundancy. The key lies in understanding the specific needs of your operations. For organizations where data accessibility and swift transaction speeds are paramount, options like RAID 0 and RAID 10 are enticing due to their high performance.
However, they must catch up in the redundancy department, a critical factor for data protection. On the other hand, RAID 5 and RAID 6 configurations offer a harmonious blend of both worlds, distributing parity data across drives to ensure no single failure leads to data loss while maintaining commendable performance levels.
All these should be determined based on the business’s needs, the frequency at which the company utilizes the data daily, and the effect of data loss. The decision should depend on your operational requirements, while the identified balance should maintain the aspects most important to your business success and data quality.
Cost Considerations and Budget Planning
Navigating the financial aspects of selecting a RAID level necessitates a careful examination of not only the initial investment but also the ongoing expenses. The price tag associated with each RAID configuration varies, reflecting differences in hardware requirements, operational efficiencies, and data protection measures.
For instance, RAID 0 may appear budget-friendly due to its minimal hardware requisites, yet its lack of redundancy could incur higher costs in the event of data loss. At the same time, RAID 6, described by its dual parity feature, ensures the integrity of the data against compromise; however, it requires more disk capacity and could cost more in the long run in terms of maintenance.
Another aspect that business people should consider is that some RAID configurations may require acquiring extra hardware and software to manage, meaning that the cost factor will be compounded. The cost elements highlighted above should be balanced with the available resources by the decision-makers to avoid selecting a RAID level that puts too much pressure on the available funds yet has to deliver on data storage and or protection.
These financial considerations will help establish fundamental parameters that meet both current and future use of storage to receive value from a RAID configuration throughout its usage duration and not hamper organized data needs.
RAID and Data Backup: Understanding the Differences
Businesses must comprehend that while RAID configurations contribute significantly to enhancing data redundancy and fault tolerance, they do not encompass all aspects of data protection. In particular, RAID is aimed at protecting against possible failure of the drive’s hardware by reading and writing data to different disks at once, which also helps to enhance the general performance of the system.
However, this method lacks the approach to recover data that might be lost due to errors not in any way associated, such as human error, software damage, malware attack, natural calamities, etc. These cases illustrate the need for an efficient backup plan that synergizes with RAID configurations.
A comprehensive backup plan ensures the recovery of critical data under circumstances RAID cannot mitigate, providing an additional layer of security. It involves creating copies of data that are stored separately from the primary storage used by the RAID array, facilitating recovery in the event of a total system compromise or failure.
Using RAID with a robust backup system prepares businesses with the best way to handle data and guard it against numerous risks that may be encountered while doing operations, even though there can be some incidents where data may be lost.
Real-World Scenarios: Choosing RAID Levels for Different Business Types
When considering real-world applications of RAID configurations, the type of business significantly influences the optimal choice. A graphic design firm, for example, where large files are routinely edited and saved, might prioritize RAID 10 for its blend of speed and redundancy, ensuring quick access to files without risking data loss.
On the other hand, a financial institution dealing with vast amounts of transaction data might lean towards RAID 6, valuing the extra layer of fault tolerance to guard against data corruption or loss. Small businesses with less intensive data needs and limited IT budgets could find RAID 1 an attractive option, providing essential redundancy at a lower cost point.
A research organization that accumulates extensive data sets over time and requires high capacity and data protection might opt for RAID 5, balancing cost, storage efficiency, and redundancy. Every business situation is different, so specific, detailed operation and data management requirements must be considered at the best RAID level. From such uses, the businesses will be able to comprehend how to undertake the configuration of RAID to suit the business’s operational environment.
Future-Proofing Your RAID Configuration
Ensuring that your RAID setup remains relevant and adaptable to the evolving demands of your business is paramount. Anticipating growth, the scalability of your selected RAID configuration becomes a critical consideration. When evaluating different RAID levels, reflect on how easily additional drives can be integrated or if transitioning to a more sophisticated RAID level without disrupting existing operations is feasible.
This thinking makes it possible to scale up or down without any hitches as the amount of data increases or where there are new high-performance demands. Furthermore, there is an issue of understanding how the changes in the RAID configuration may impact the elements that can be associated with the given system, namely its speeds and its levels of redundancy.
An initial RAID configuration that offers scalability and flexibility without a significant compromise in these areas ensures that your data storage system remains robust and efficient, even as your business needs evolve. In addition to such considerations, it also helps mitigate potential future problems on the way to getting the highest ROI on your storage investments – the ability of your storage to evolve with your company.